01.实现二叉树
目录介绍
- 01.二叉查找树节点的定义
- 02.二叉树遍历
- 03.二叉树查找
- 04.最大值和最小值
- 05.前驱和后继
- 06.插入和删除
01.二叉查找树节点的定义
- 代码如下所示
public class BSTree<T extends Comparable<T>> { private BSTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点 public class BSTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> { T key; // 关键字(键值) BSTNode<T> left; // 左孩子 BSTNode<T> right; // 右孩子 BSTNode<T> parent; // 父结点 public BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent, BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right) { this.key = key; this.parent = parent; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } ...... } - BSTree是二叉树,它保含了二叉树的根节点mRoot;mRoot是BSTNode类型,而BSTNode是二叉查找树的节点,它是BSTree的内部类。BSTNode包含二叉查找树的几个基本信息:
- (01) key -- 它是关键字,是用来对二叉查找树的节点进行排序的。
- (02) left -- 它指向当前节点的左孩子。
- (03) right -- 它指向当前节点的右孩子。
- (04) parent -- 它指向当前节点的父结点。
02.二叉树遍历
- 如何将二叉树的所有节点遍历打印出来?经典的有三种方法:前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。其中,前、中、后序,表示的是节点与它的左右子树节点的遍历打印先后顺序。
- 前序遍历:对于树中任意节点,先打印这个节点,再打印它的左子树,再打印它的右子树。
- 中序遍历:对于树中任意节点,先打印左子树,再打印它本身,最后打印右子树。
- 后序遍历:对于树中任意节点,先打印左子树,再打印右子树,最后打印它本身。
- 如图所示
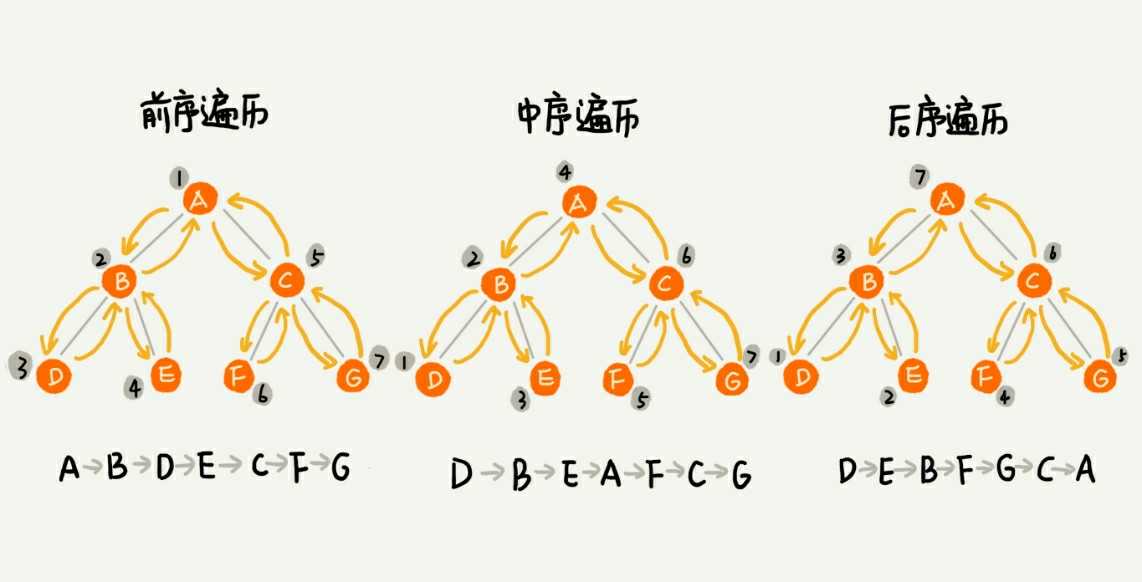
image
2.1 前序遍历
- 若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
- (01) 访问根结点;
- (02) 先序遍历左子树;
- (03) 先序遍历右子树。
- 前序遍历代码
private void preOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if(tree != null) { System.out.print(tree.key+" "); preOrder(tree.left); preOrder(tree.right); } } public void preOrder() { preOrder(mRoot); }
2.2 中序遍历
- 若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
- (01) 中序遍历左子树;
- (02) 访问根结点;
- (03) 中序遍历右子树。
- 中序遍历代码
private void inOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if(tree != null) { inOrder(tree.left); System.out.print(tree.key+" "); inOrder(tree.right); } } public void inOrder() { inOrder(mRoot); }
2.3 后序遍历
- 若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
- (01) 后序遍历左子树;
- (02) 后序遍历右子树;
- (03) 访问根结点。
- 后序遍历代码
private void postOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if(tree != null) { postOrder(tree.left); postOrder(tree.right); System.out.print(tree.key+" "); } } public void postOrder() { postOrder(mRoot); }
2.4 遍历结果分析
- 看看下面这颗树的各种遍历方式:

img
- 对于上面的二叉树而言,
- (01) 前序遍历结果: 3 1 2 5 4 6
- (02) 中序遍历结果: 1 2 3 4 5 6
- (03) 后序遍历结果: 2 1 4 6 5 3
03.二叉树查找
- 递归版本的代码
/* * (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { if (x==null) return x; int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) return search(x.left, key); else if (cmp > 0) return search(x.right, key); else return x; } public BSTNode<T> search(T key) { return search(mRoot, key); } - 非递归版本的代码
/* * (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { while (x!=null) { int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else if (cmp > 0) x = x.right; else return x; } return x; } public BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) { return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key); }
04.最大值和最小值
- 查找最大值的代码
/* * 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> maximum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while(tree.right != null) tree = tree.right; return tree; } public T maximum() { BSTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return null; } - 查找最小值的代码
/* * 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> minimum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while(tree.left != null) tree = tree.left; return tree; } public T minimum() { BSTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return null; }
05.前驱和后继
- 节点的前驱:是该节点的左子树中的最大节点。
- 节点的后继:是该节点的右子树中的最小节点。
- 查找前驱节点的代码
/* * 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> predecessor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。 if (x.left != null) return maximum(x.left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (02) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y!=null) && (x==y.left)) {//满足条件,不断往上追溯,直到找到右祖先结点 x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; } - 查找后继节点的代码
/* * 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。 if (x.right != null) return minimum(x.right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y!=null) && (x==y.right)) {//满足条件,不断往上追溯,直到找到右祖先结点 x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; }
06.插入和删除
- 插入节点的代码
/* * 将结点插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的 * z 插入的结点 */ private void insert(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { int cmp; BSTNode<T> y = null; BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot; // 查找z的插入位置 while (x != null) { y = x; cmp = z.key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else x = x.right; } z.parent = y; if (y==null) bst.mRoot = z; else { cmp = z.key.compareTo(y.key); if (cmp < 0) y.left = z; else y.right = z; } } /* * 新建结点(key),并将其插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * key 插入结点的键值 */ public void insert(T key) { BSTNode<T> z=new BSTNode<T>(key,null,null,null); // 如果新建结点失败,则返回。 if (z != null) insert(this, z); }- 注:本文实现的二叉查找树是允许插入相同键值的节点的。
- 删除节点的代码
/* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * bst 二叉树 * z 删除的结点 */ private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { BSTNode<T> x=null; BSTNode<T> y=null; if ((z.left == null) || (z.right == null) ) y = z; else y = successor(z); if (y.left != null) x = y.left; else x = y.right; if (x != null) x.parent = y.parent; if (y.parent == null) bst.mRoot = x; else if (y == y.parent.left) y.parent.left = x; else y.parent.right = x; if (y != z) z.key = y.key; return y; } /* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * z 删除的结点 */ public void remove(T key) { BSTNode<T> z, node; if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != null) if ( (node = remove(this, z)) != null) node = null; }
07.打印和销毁
- 打印二叉查找树的代码
/* * 打印"二叉查找树" * * key -- 节点的键值 * direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点; * -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子; * 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。 */ private void print(BSTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) { if(tree != null) { if(direction==0) // tree是根节点 System.out.printf("%2d is root\n", tree.key); else // tree是分支节点 System.out.printf("%2d is %2d's %6s child\n", tree.key, key, direction==1?"right" : "left"); print(tree.left, tree.key, -1); print(tree.right,tree.key, 1); } } public void print() { if (mRoot != null) print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0); } - 销毁二叉查找树的代码
/* * 销毁二叉树 */ private void destroy(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree==null) return ; if (tree.left != null) destroy(tree.left); if (tree.right != null) destroy(tree.right); tree=null; } public void clear() { destroy(mRoot); mRoot = null; }
08.深度/广度遍历
- 树的深度优先遍历需要用到额外的数据结构--->栈;而广度优先遍历需要队列来辅助;这里以二叉树为例来实现。
import java.util.ArrayDeque; public class BinaryTree { static class TreeNode{ int value; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode(int value){ this.value=value; } } TreeNode root; public BinaryTree(int[] array){ root=makeBinaryTreeByArray(array,1); } /** * 采用递归的方式创建一颗二叉树 * 传入的是二叉树的数组表示法 * 构造后是二叉树的二叉链表表示法 */ public static TreeNode makeBinaryTreeByArray(int[] array,int index){ if(index<array.length){ int value=array[index]; if(value!=0){ TreeNode t=new TreeNode(value); array[index]=0; t.left=makeBinaryTreeByArray(array,index*2); t.right=makeBinaryTreeByArray(array,index*2+1); return t; } } return null; } /** * 深度优先遍历,相当于先根遍历 * 采用非递归实现 * 需要辅助数据结构:栈 */ public void depthOrderTraversal(){ if(root==null){ System.out.println("empty tree"); return; } ArrayDeque<TreeNode> stack=new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>(); stack.push(root); while(stack.isEmpty()==false){ TreeNode node=stack.pop(); System.out.print(node.value+" "); if(node.right!=null){ stack.push(node.right); } if(node.left!=null){ stack.push(node.left); } } System.out.print("\n"); } /** * 广度优先遍历 * 采用非递归实现 * 需要辅助数据结构:队列 */ public void levelOrderTraversal(){ if(root==null){ System.out.println("empty tree"); return; } ArrayDeque<TreeNode> queue=new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>(); queue.add(root); while(queue.isEmpty()==false){ TreeNode node=queue.remove(); System.out.print(node.value+" "); if(node.left!=null){ queue.add(node.left); } if(node.right!=null){ queue.add(node.right); } } System.out.print("\n"); } /** * 13 * / \ * 65 5 * / \ \ * 97 25 37 * / /\ / * 22 4 28 32 */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr={0,13,65,5,97,25,0,37,22,0,4,28,0,0,32,0}; BinaryTree tree=new BinaryTree(arr); tree.depthOrderTraversal(); tree.levelOrderTraversal(); } }
其他内容
01.关于博客汇总链接
02.关于我的博客
- github:https://github.com/yangchong211
- 知乎:https://www.zhihu.com/people/yczbj/activities
- 简书:http://www.jianshu.com/u/b7b2c6ed9284
- csdn:http://my.csdn.net/m0_37700275
- 喜马拉雅听书:http://www.ximalaya.com/zhubo/71989305/
- 开源中国:https://my.oschina.net/zbj1618/blog
- 泡在网上的日子:http://www.jcodecraeer.com/member/content_list.php?channelid=1
- 邮箱:yangchong211@163.com
- 阿里云博客:https://yq.aliyun.com/users/article?spm=5176.100- 239.headeruserinfo.3.dT4bcV
- segmentfault头条:https://segmentfault.com/u/xiangjianyu/articles
- 掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5939433efe88c2006afa0c6e
